From Wiki
Diffuse sky radiation is solar radiation reaching the earth's surface after having been scattered from the direct solar beam by molecules or suspensoids in the atmosphere. Also called skylight, diffuse skylight, or sky radiation. Of the total light removed from the direct solar beam by scattering in the atmosphere (approximately 25 percent of the incident radiation), about two-thirds ultimately reaches the earth as diffuse sky radiation.
Scattering is the process by which small particles suspended in a medium of a different index of refraction redirect a portion of the incident radiation in all directions. In elastic scattering, no energy transformation results, only a change in the spatial distribution of the radiation. The science of optics usually uses the term to refer to the deflection of photons that occurs when they are absorbed and re-emitted by atoms or molecules.
Why is the sky blue?
The sky is blue partly because air scatters short-wavelength light in preference to longer wavelengths. Combined, these effects scatter (bend away in all directions) some short, blue light waves while allowing almost all longer, red light waves to pass straight through. When we look toward a part of the sky not near the sun, the blue color we see is blue light waves scattered down toward us from the white sunlight passing through the air overhead. Near sunrise and sunset, most of the light we see comes in nearly tangent to the Earth's surface, so that the light's path through the atmosphere is so long that much of the blue and even yellow light is scattered out, leaving the sun rays and the clouds it illuminates red.
Scattering and absorption are major causes of the attenuation of radiation by the atmosphere. Scattering varies as a function of the ratio of the particle diameter to the wavelength of the radiation. When this ratio is less than about one-tenth, Rayleigh scattering occurs in which the scattering coefficient varies inversely as the fourth power of the wavelength. At larger values of the ratio of particle diameter to wavelength, the scattering varies in a complex fashion described, for spherical particles, by the Mie theory; at a ratio of the order of 10, the laws of geometric optics begin to apply.
Why is the sky blue instead of violet?

Normalized typical human cone responses (and the rod response) to monochromatic spectral stimuli
Because of the strong wavelength dependence (inverse fourth power) of light scattering according to Raleigh's Law, one would expect that the sky would appear more violet than blue, the former having a shorter wavelength than the latter. There is a simple physiological explanation for this apparent conundrum. Simply put, the human eye cannot detect violet light in presence of light with longer wavelengths. There is a reason for this. It turns out that the human eye's high resolution color-detection system is made of proteins and chromophores (which together make up photoreceptor cells or "Cone" structures in the eye's fovea) that are sensitive to different wavelengths in the visible spectrum (400 nm–700 nm). In fact, there are three major protein-chromophore sensors that have peak sensitivities to yellowish-green (564 nm), bluish-green (534 nm), and blue-violet (420 nm) light. The brain uses the different responses of these chromophores to interpret the spectrum of the light that reaches the retina.
When one experimentally plots the sensitivity curves for the three color sensors (identified here as long (L), middle (M), and short (S) wavelength), three roughly "bell-curve" distributions are seen to overlap one another and cover the visible spectrum. We depend on this overlap for color sensing to detect the entire spectrum of visible light. For example, monochromatic violet light at 400 nm mostly stimulates the S receptors, but also slightly stimulates the L and M receptors, with the L receptor having the stronger response. This combination of stimuli is interpreted by the brain as violet. Monochromatic blue light, on the other hand, stimulates the M receptor more than the L receptor. Skylight is not monochromatic; it contains a mixture of light covering much of the spectrum. The combination of strong violet light with weaker blue and even weaker green and yellow strongly stimulates the S receptor, and stimulates the M receptor more than the L receptor. As a result, this mixture of wavelengths is perceived by the brain as blue rather than violet.
Neutral points
There are three commonly detectable points of zero polarization of diffuse sky radiation (known as neutral points) lying along the vertical circle through the sun.
- The Arago point, named for its discoverer, is customarily located at about 20° above the antisolar point; but it lies at higher altitudes in turbid air. The latter property makes the Arago distance a useful measure of atmospheric turbidity.
- The Babinet point, discovered by Babinet in 1840, typically lies only 15° to 20° above the sun, and hence is difficult to observe because of solar glare.
- The Brewster point, discovered by Brewster in 1840, is located about 15° to 20° directly below the sun; hence it is difficult to observe because of the glare of the sun.
Under an overcast sky
There is essentially zero direct sunlight under an overcast sky, so all light is then diffuse sky radiation. The flux of light is not very wavelength dependent because the cloud droplets are larger than the light's wavelength and scatter all colors approximately equally. The light passes through the translucent clouds in a manner similar to frosted glass. The intensity ranges (roughly) from 1/6 of direct sunlight for relatively thin clouds down to 1/1000 of direct sunlight under the extreme of thickest storm clouds.
See also
External links
Books
***************
[Physics FAQ] -
[Copyright] Original by Philip Gibbs May 1997.
A clear cloudless day-time sky is blue because molecules in the air scatter blue light from the sun more than they scatter red light. When we look towards the sun at sunset, we see red and orange colours because the blue light has been scattered out and away from the line of sight.

The white light from the sun is a mixture of all colours of the rainbow. This was demonstrated by Isaac Newton, who used a prism to separate the different colours and so form a spectrum. The colours of light are distinguished by their different wavelengths. The visible part of the spectrum ranges from red light with a wavelength of about 720 nm, to violet with a wavelength of about 380 nm, with orange, yellow, green, blue and indigo between. The three different types of colour receptors in the retina of the human eye respond most strongly to red, green and blue wavelengths, giving us our colour vision.
Tyndall Effect
The first steps towards correctly explaining the colour of the sky were taken by John Tyndall in 1859. He discovered that when light passes through a clear fluid holding small particles in suspension, the shorter blue wavelengths are scattered more strongly than the red. This can be demonstrated by shining a beam of white light through a tank of water with a little milk or soap mixed in. From the side, the beam can be seen by the blue light it scatters; but the light seen directly from the end is reddened after it has passed through the tank. The scattered light can also be shown to be polarised using a filter of polarised light, just as the sky appears a deeper blue through polaroid sun glasses.
This is most correctly called the Tyndall effect, but it is more commonly known to physicists as Rayleigh scattering--after Lord Rayleigh, who studied it in more detail a few years later. He showed that the amount of light scattered is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength for sufficiently small particles. It follows that blue light is scattered more than red light by a factor of (700/400)4 ~= 10.
Dust or Molecules?
Tyndall and Rayleigh thought that the blue colour of the sky must be due to small particles of dust and droplets of water vapour in the atmosphere. Even today, people sometimes incorrectly say that this is the case. Later scientists realised that if this were true, there would be more variation of sky colour with humidity or haze conditions than was actually observed, so they supposed correctly that the molecules of oxygen and nitrogen in the air are sufficient to account for the scattering. The case was finally settled by Einstein in 1911, who calculated the detailed formula for the scattering of light from molecules; and this was found to be in agreement with experiment. He was even able to use the calculation as a further verification of Avogadro's number when compared with observation. The molecules are able to scatter light because the electromagnetic field of the light waves induces electric dipole moments in the molecules.
Why not violet?
If shorter wavelengths are scattered most strongly, then there is a puzzle as to why the sky does not appear violet, the colour with the shortest visible wavelength. The spectrum of light emission from the sun is not constant at all wavelengths, and additionally is absorbed by the high atmosphere, so there is less violet in the light. Our eyes are also less sensitive to violet. That's part of the answer; yet a rainbow shows that there remains a significant amount of visible light coloured indigo and violet beyond the blue. The rest of the answer to this puzzle lies in the way our vision works. We have three types of colour receptors, or cones, in our retina. They are called red, blue and green because they respond most strongly to light at those wavelengths. As they are stimulated in different proportions, our visual system constructs the colours we see.
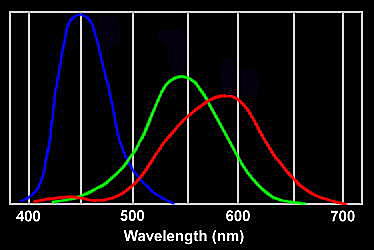
Response curves for the three types of cone in the human eye
When we look up at the sky, the red cones respond to the small amount of scattered red light, but also less strongly to orange and yellow wavelengths. The green cones respond to yellow and the more strongly-scattered green and green-blue wavelengths. The blue cones are stimulated by colours near blue wavelengths which are very strongly scattered. If there were no indigo and violet in the spectrum, the sky would appear blue with a slight green tinge. However, the most strongly scattered indigo and violet wavelengths stimulate the red cones slightly as well as the blue, which is why these colours appear blue with an added red tinge. The net effect is that the red and green cones are stimulated about equally by the light from the sky, while the blue is stimulated more strongly. This combination accounts for the pale sky blue colour. It may not be a coincidence that our vision is adjusted to see the sky as a pure hue. We have evolved to fit in with our environment; and the ability to separate natural colours most clearly is probably a survival advantage.

A multi-coloured sunset over the Firth of Forth in Scotland.
Sunsets
When the air is clear the sunset will appear yellow, because the light from the sun has passed a long distance through air and some of the blue light has been scattered away. If the air is polluted with small particles, natural or otherwise, the sunset will be more red. Sunsets over the sea may also be orange, due to salt particles in the air, which are effective Tyndall scatterers. The sky around the sun is seen reddened, as well as the light coming directly from the sun. This is because all light is scattered relatively well through small angles--but blue light is then more likely to be scattered twice or more over the greater distances, leaving the yellow, red and orange colours.

A blue haze over the mountains of Les Vosges in France.
Blue Haze and Blue Moon
Clouds and dust haze appear white because they consist of particles larger than the wavelengths of light, which scatter all wavelengths equally (Mie scattering). But sometimes there might be other particles in the air that are much smaller. Some mountainous regions are famous for their blue haze. Aerosols of terpenes from the vegetation react with ozone in the atmosphere to form small particles about 200 nm across, and these particles scatter the blue light. A forest fire or volcanic eruption may occasionally fill the atmosphere with fine particles of 500-800 nm across, being the right size to scatter red light. This gives the opposite to the usual Tyndall effect, and may cause the moon to have a blue tinge since the red light has been scattered out. This is a very rare phenomenon--occurring literally once in a blue moon.
Opalescence
The Tyndall effect is responsible for some other blue coloration's in nature: such as blue eyes, the opalescence of some gem stones, and the colour in the blue jay's wing. The colours can vary according to the size of the scattering particles. When a fluid is near its critical temperature and pressure, tiny density fluctuations are responsible for a blue coloration known as critical opalescence. People have also copied these natural effects by making ornamental glasses impregnated with particles, to give the glass a blue sheen. But not all blue colouring in nature is caused by scattering. Light under the sea is blue because water absorbs longer wavelength of light through distances over about 20 metres. When viewed from the beach, the sea is also blue because it reflects the sky, of course. Some birds and butterflies get their blue colorations by diffraction effects.
Why is the Mars sky red?
Images sent back from the Viking Mars landers in 1977 and from Pathfinder in 1997 showed a red sky seen from the Martian surface. This was due to red iron-rich dusts thrown up in the dust storms occurring from time to time on Mars. The colour of the Mars sky will change according to weather conditions. It should be blue when there have been no recent storms, but it will be darker than the earth's daytime sky because of Mars' thinner atmosphere.


















